The semiconductors used in automotive electronics, i.e., automotive-grade chips, mainly consist of four major categories, namely, main control chips (MCU/SoC), power chips (IGBT), sensor chips (CIS) and memory chips (Flash). Automotive-grade chips are widely used in automotive powertrain systems, intelligent cockpits and self-driving systems, and they are indispensable core components for automotive electronics.
1、Introduction of MCU
MCU that is, Micro Control Unit (Micro Controller Unit), also known as Single Chip Microcomputer (Single Chip Microcomputer), is the CPU, storage, peripheral functions are integrated in a single chip with the control function of the chip computer, as a highly integrated microcomputer control system, microcontroller has a simple system structure, high reliability, strong processing capabilities, low voltage and low power consumption, strong environmental adaptability and other characteristics, has been widely used in automotive electronics, industrial control, instrumentation, home appliances and other fields. As a highly integrated microcomputer control system, microcontroller has the features of simple system structure, high reliability, strong processing function, low voltage and low power consumption, and strong environmental adaptability, etc. It has been widely used in the fields of automotive electronics, industrial control, instrumentation, home appliances, and so on.
In the various systems of automotive electronics, it is often necessary to use automotive MCU (automotive microcontroller) as the core of the operation and control, responsible for a variety of information computing and processing, used in automotive powertrain, assisted driving, network interconnectivity, chassis safety, infotainment, and body electronics and other directions.
1. Basic structure of MCU
Several important components that make up an MCU include:
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is the brain of the MCU. It consists of the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and the Control Unit (CU).The CPU reads, decodes, and executes instructions to perform arithmetic, logic, and data transfer operations.
Memory Units
Any computing system requires two types of memory: program memory and data memory. Program memory, as the name suggests, contains the program, i.e., the instructions to be executed by the CPU. On the other hand, data memory is needed to store temporary data while instructions are being executed. Typically, program memory is read-only memory (ROM) and data memory is random access memory (RAM).
Input/Output Ports
The interface between the microcontroller and the external world is provided by input/output ports (I/O ports). Input devices such as switches, keyboards, etc. provide information in the form of binary data from the user to the CPU.The CPU, after receiving data from the input devices, executes the appropriate commands and responds by means of output devices such as LEDs, displays, and printers.
Timer/Counter
One of the important components of a microcontroller is timers and counters. They provide the operation of time delay and counting of external events. In addition, timers and counters can provide function generation, pulse width modulation, clock control etc.
Bus
Another important component of a microcontroller, but rarely talked about, is the system bus. The system bus is a set of connecting wires that connects the CPU to other peripheral devices such as memory, I/O ports, and other supporting components.
2. How MCU works
The working principle of MCU is the process of executing pre-stored instructions one by one. Different types of microcontrollers have different instruction systems. In order for a microcontroller function to accomplish a specific task automatically, the problem to be solved must be coded into a series of instructions, and these instructions must be recognized and executed by a separate function, so that the collection of a series of instructions becomes a program, which need to be pre-stored in memory with storage capacity, that is, memory.
Since the program is executed sequentially, the instructions in the program are also stored one by one, the MCU has to extract and execute these instructions one by one when executing the program, and it must have the function of being able to keep track of the storage unit where the instructions are located, and this part is the Program Counter PC (including the CPU), when the program starts to run, the PC will be assigned to the storage unit of each instruction in the program, and one by one, the contents of the PC will automatically increase. When the program starts to run, PC will be assigned to the memory cell of each instruction in the program, and execute the instruction one by one, the content in PC will be increased automatically, and the amount of increase will be determined by the length of this instruction, and each of them will point to the starting address of the next instruction, which ensures the sequential execution of instructions.
Kernel architecture is a key element that affects the performance of MCUs, and better computing units require more advanced kernel architecture. More than ten years ago, the major MCU manufacturers are using their own kernel, such as Renesas RX core, Freescale PowerPC, Microchip PIC, Atmel AVR, with the introduction of the ARM Cortex-M architecture and carry out a unique pioneering IP licensing model, with its software code sharing and high compatibility, high-density instruction set and other characteristics, has gradually occupied the dominant position. dominant position.
3. Types of automotive MCUs
Automotive MCUs can be categorized into 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit according to the number of bits. The number of bits is the width of MCU single processing data, the higher the number of bits, the stronger the performance of the MCU. 8-bit MCU cost/power consumption is low, easy to develop, the performance can meet the needs of most scenarios, and is widely used in the field of basic functions such as fan, windshield wipers, sunroofs, seat control, etc. 32-bit MCU has stronger computing power to meet the needs of high-speed processing, which is mostly used for solving complex scenarios such as automotive intelligent cockpit, body control, assisted driving, traveling, etc., 32-bit CPU kernel with ARM as the mainstream architecture, due to the CPU instruction set is huge, software development is difficult, the unit price is generally several times higher than the 8-bit MCU, and thus also has a higher R & D barriers.
Since the program is executed sequentially, the instructions in the program are also stored one by one, the MCU has to extract and execute these instructions one by one when executing the program, and it must have the function of being able to keep track of the storage unit where the instructions are located, and this part is the Program Counter PC (including the CPU), when the program starts to run, the PC will be assigned to the storage unit of each instruction in the program, and one by one, the contents of the PC will automatically increase. When the program starts to run, PC will be assigned to the memory cell of each instruction in the program, and execute the instruction one by one, the content in PC will be increased automatically, and the amount of increase will be determined by the length of this instruction, and each of them will point to the starting address of the next instruction, which ensures the sequential execution of instructions.
Kernel architecture is a key element that affects the performance of MCUs, and better computing units require more advanced kernel architecture. More than ten years ago, the major MCU manufacturers are using their own kernel, such as Renesas RX core, Freescale PowerPC, Microchip PIC, Atmel AVR, with the introduction of the ARM Cortex-M architecture and carry out a unique pioneering IP licensing model, with its software code sharing and high compatibility, high-density instruction set and other characteristics, has gradually occupied the dominant position. dominant position.
3. Types of automotive MCUs
Automotive MCUs can be categorized into 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit according to the number of bits. The number of bits is the width of MCU single processing data, the higher the number of bits, the stronger the performance of the MCU. 8-bit MCU cost/power consumption is low, easy to develop, the performance can meet the needs of most scenarios, and is widely used in the field of basic functions such as fan, windshield wipers, sunroofs, seat control, etc. 32-bit MCU has stronger computing power to meet the needs of high-speed processing, which is mostly used for solving complex scenarios such as automotive intelligent cockpit, body control, assisted driving, traveling, etc., 32-bit CPU kernel with ARM as the mainstream architecture, due to the CPU instruction set is huge, software development is difficult, the unit price is generally several times higher than the 8-bit MCU, and thus also has a higher R & D barriers.
III.MCU Market Situation
1. Market Size
According to IC Insights, the global MCU market size grew from $15.9 billion in 2015 to $22.1 billion in 2021, with a CAGR of 5.6%; the global MCU market size is expected to reach $23.9 billion in 2022, with a year-on-year growth rate of 8.1%.MCU is one of the key components for the in-depth development of automobiles from electrification to intelligence, and automobiles are also the world's MCU first application market, accounting for more than 1/3, the average demand for MCU per car is as high as hundreds. With the automotive semiconductor industry technology evolution and demand upgrading, intelligent will gradually become the main battlefield of the relevant manufacturers competition, relay electrification has become an important driving force, MCU as the core computing chip depth benefit.
Source: IC Insights, Prospect Research Institute, Donghai Securities Research Institute
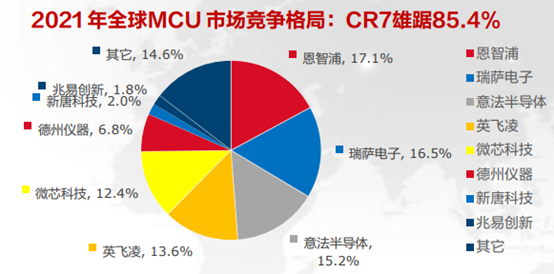
2. Competitive landscape
According to Omdia, the MCU market is mainly held firmly by European, American and Japanese chip makers, with the top seven makers accounting for 85.4% of the global market share, but the share of each company is relatively more even. As for the domestic MCU market, according to CSIA and China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), in 2021, about 85% of the domestic MCU market (94% in 2019) will be held by foreign investors, with a low localization rate of MCUs and mostly concentrated in the consumer level, and the self-sufficiency rate of automotive-grade MCUs is still less than 5%, which is still a large space for domestic substitution.
According to Future Electronics, global automotive semiconductors are still in short supply in the fourth quarter of 2022, with major automotive MCU makers such as STMicroelectronics, NXP, and Microchip Technology experiencing varying degrees of supply constraints, and both chip prices and shipment schedules have risen significantly over the previous two quarters. Overseas manufacturers of production capacity expansion can not meet market demand, domestic MCU companies are expected to grasp this mismatch between supply and demand window of time, with the previous investment, and the domestic downstream car-making new forces to accelerate the process of domestic substitution of automotive-grade MCU.
MCU technology development trend
1. Higher computing power
With the increasing degree of automotive intelligence, automotive-grade MCUs will develop in the direction of multi-functional integration, high arithmetic power and ultra-low power consumption, and the number of uses will also increase. At the same time, a large number of car sensors and car cameras used in future smart cars also require high-performance MCUs to do analog data processing and drive control. Therefore, in the future higher-order autonomous driving level of the car, and multi-sensor fusion trend, the bus width of 32-bit or even 64-bit high-computing power automotive-grade MCU will become the mainstream products, while 8/16-bit low-end MCU will be integrated by the higher process SOC, losing growth momentum.
2. Higher integration
Due to the integration of more functions, the arithmetic power requirements of the main control chip will rise exponentially, and part of the MCU will be integrated into the SoC (System-on-Chip) together with different types of chips such as GPU, DSP, NPU and AI processing unit, etc. The SoC is the result of higher integration of MCUs, which has more complex functions and more efficient utilization of resources, and it can be capable of handling scenarios such as unmanned vehicles and smart cockpits, etc., which require high arithmetic power.
3. Higher Openness
Due to the high IP license fee of ARM core, many vendors have started to develop MCU based on open source RISC-V core, such as Renesas, Intel, Mega Innovation, etc. RISC-V is not only completely free and open source, but also has the characteristics of low power consumption, streamlined instruction set, simple design and compilation, and support for modularization and scalability, which is a perfect match with the characteristics of automotive-grade MCUs, such as fragmentation of scenarios and modularization of functions. This is a perfect match with the fragmentation and modularization of automotive MCUs.