With the rapid development of Internet of Things, cloud computing, big data and other technologies, mankind is entering another "data age" from the "information age". In order to better manage these rich and huge data assets, higher requirements are put forward for memory chips.
The Importance of Storage in the Age of Big Data
Since 2018, the data generated by machines has exceeded the data generated by human beings, which is the first time in human history. It is estimated that by 2022, the data generated by machines will be nine times as much as that generated by humans. All data, including data generated by unmanned vehicles, smart cities, smart homes and other machines, must be transmitted from terminals and edges through various layers, calculated to the cloud and big data center, then calculated, and finally returned to the terminal. All processes require huge computing power. The existing computing architecture can no longer meet the needs of further development, so we pay more attention to the development of storage.
Dynamic randomly access memory (DRAM) came out in 1966, and the memory entered the semiconductor era. The earliest single Die (Die) capacity was 1kb, and now it has reached 16Gb and above. Until 1980, Toshiba invented Flash, and then in 1990s, many Flash applications such as USB and SD card appeared successively. In 2008, 3D flash memory (NAND) technology sprouted, and it was officially commercialized and mass-produced in 2014.
Therefore, semiconductor memory has been developed for 55 years, including DRAM for 55 years and Flash for 40 years. Because of the huge difference between 2D NAND and 3D NAND technology, in fact, 3D NAND has only developed for more than ten years, and its technology maturity is far less than DRAM.
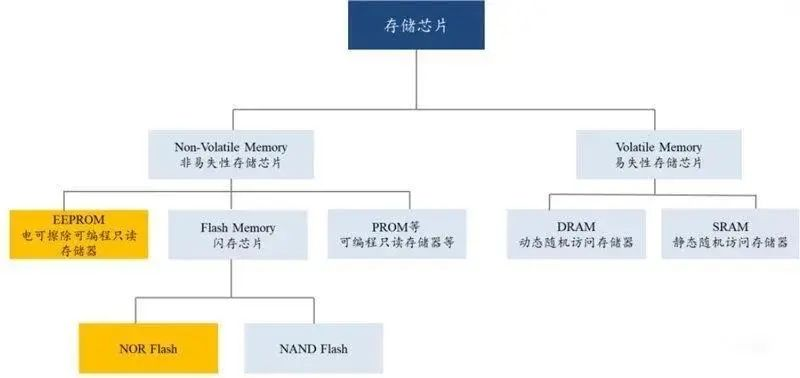
Generally speaking, semiconductor memory can be divided into two categories: volatile memory and nonvolatile memory. Among them, "volatile memory" refers to the memory where memory information is lost after power failure, such as DRAM, including memory chips in computers; The "non-volatile memory" refers to the memory where the memory information still exists after power failure, mainly including NOR Flash and NAND Flash, which have the characteristics of small size and fast storage speed.
Source: Zhidx
The necessity of memory chips lies in their size and importance. "Big" is reflected in the fact that its market scale is large enough, accounting for about one-third of the total semiconductor market, and it is applied in memory, consumer electronics, smart terminals and other fields; "Important" is reflected in the fact that the memory chip is the granary of electronic system and the carrier of data, which is related to the safety of data.
With entering the era of cloud computing and big data, memory chips have become a strategic emerging industry related to the success or failure of the next generation of information technology. Memory chips are related to national information security, information technology industry chain security, and even the development of higher-order artificial intelligence in the future.
Localized memory chips are gradually rising
Chinese mainland is a big consumer of memory chips. China imports more than 300 billion US dollars of chips every year, of which memory chips account for more than 30%, consuming nearly 50% of the global memory capacity. However, such a huge domestic market faces multiple difficulties and challenges.
First, strong computing power, super Moore's Law technical challenges, and high costs put forward higher requirements for memory chips, which also makes it a big problem to achieve mass production; Second, the memory chip industry in Chinese mainland has been hit by the precise blockade of the combination boxing of the US government. The US Department of Commerce (BIS) issued a series of policies prohibiting US suppliers from providing production equipment to manufacturers of DRAM and 3D NAND memory chips in Chinese mainland; Third, the accumulation of memory chip-related technologies in Chinese mainland is weak, the self-sufficiency is less than 10%, and the localization is very low.

Based on the independent and controllable policy requirements, Chinese mainland manufacturers have faced difficulties and started the strategic layout of memory chips. For example, domestic enterprises such as Yangtze Memory, Jinhua and CXMT have made continuous breakthroughs in technology and contributed their own strength to promote chip made in China.
In August, 2018, Yangtze Memory released Xtacking technology, which successfully achieved breakthrough innovation in flash memory technology architecture. In 2020, Yangtez Momory has achieved 128-layer NAND mass production, which is no different from Samsung and other foreign manufacturers. In 2021, Yangtze Memory accounted for about 5% of the global market share, second only to Samsung, SK Hynix, Kioxia, Western Data and Micron, and became the sixth largest NAND flash memory manufacturer in the world.
The second phase of Yangtze Memory is planned to be put into production as early as the end of 2022, with an estimated production capacity of 200,000 wafers/month. However, due to the depression of the global semiconductor market and the downward cycle, and the semiconductor control policy of the United States, Yangtze Memory was affected by it, and this plan was temporarily suspended.
Recently, with the latest financial reports of major semiconductor manufacturers released, the revenues of many enterprises fell short of expectations, and the performance of giants such as Intel, Samsung, Micron and SK Hynix declined significantly. According to industry sources, almost every memory chip produced by major storage companies is losing money, and the collective operating loss in 2023 is estimated to reach a record 5 billion US dollars.

Source: Samsung Electronics Financial Report, profit plummeted by 97%
In addition to the decline in global demand and economic growth, China's memory chips are gradually self-produced, and domestic enterprises are gradually reducing their purchases of memory chips from Korea, Taiwan and Japan, which may also be the reason for the high inventory and weak demand of memory chips of several giants.
Application of Advanced Packaging in Memory Devices
Domestic chip companies are also facing multiple challenges. With the continuous development of chip miniaturization, the process begins to advance towards smaller process. In this case, advanced packaging and testing technology is an important development direction of future storage technology.
The packaging process of memory chips is mainly divided into wafer ultra-thin grinding, stacking and loading, wire bonding and back-end packaging. Among them, "wafer grinding" is one of the three keys of storage technology, and its main purpose is to thin and cut silicon wafers. This is very important for the development of lightweight and miniaturization of memory packages. However, thinner chips require higher level of process capability and control, which makes many package manufacturers face great challenges.

Source: Tensun
The thinner the thickness of the chip, the more brittle the strength of the chip. The traditional grinding and scratching process is easy to produce chip cracks. This is because the traditional mechanical cutting will produce stress in the chip, which will lead to some damage to the chip, such as side collapse, fragmentation, etc. The thinner the thickness of the thinned wafer, the greater its warpage, which is easy to cause wafer fracture. Of course, apart from warping and fragmentation, in the process of chip packaging, any tiny particle is fatal, which is likely to lead to chip fragmentation, thus making the whole product scrapped. Therefore, it is particularly important to control cleanliness in the production process.
In view of the above problems, Tensun abandons the traditional grinding and scratching process which has limitations on chip thickness. By setting precise components, it can accurately cut materials and carefully clean materials after cutting, thus reducing the trouble of cleaning materials in the later stage and improving production efficiency. Tensun deeply explores the market of precision cutting machines. Different cutting equipment is suitable for cutting requirements of different types of materials and sizes, meets the packaging and testing requirements of memory chips at the back end, and helps the development of domestic memory chips.
Opportunities and challenges in the era of big data: the gradual rise of domestic memory chips-China.exportsemi.com)






