The Assumed Profit Model for End-User Energy Storage Products
In the economic analysis of household storage, the first three products are photovoltaic, energy storage and optical storage integrated machine
There are two sources of income for photovoltaic and energy storage: power generation or discharge is used to save electricity bills, and surplus electricity is sold to the power grid to earn electricity bills.
- Household electricity charges are higher than on-line electricity charges, so the most economical way for consumers to use photovoltaic/energy storage is to use all power generation for electricity charges offset. Taking China as an example, in 2020, the average electricity consumption of residents in China will be 0.51 yuan/kWh, while the on-grid electricity price after subsidy will be 0.41 yuan/kWh.
- Photovoltaic power generation and power load have time dislocation, so they can't be used for their own use. Photovoltaic output is mainly concentrated at noon, while the peak power consumption on the load side is concentrated between 8-10:00 in the morning and 6-10:00 in the evening. The mismatch between power generation and power consumption will lead to the fact that even if photovoltaic power generation is less than domestic power consumption, it may not be fully used for electricity saving.
- Off-peak electricity price generally appears from evening to morning (at this time, the demand for electricity is less and the electricity price is lower). After energy storage charging, the first peak discharge has the greatest economic benefit, and the second charging (if there is no photovoltaic) will appear in normal charging.
- There is a possibility of excess solar power generation and energy storage capacity. When household electricity consumption is low, the stored energy can be fed back into the grid to earn electricity fees.

Figure 1: The revenue sources of photovoltaic and energy storage are mainly divided into two types
Operation mode and profit mode of photovoltaic, energy storage and optical storage integrated products
- In the context of standalone solar power, after solar power generation during the day, a portion can be used for household consumption. However, during periods when solar power generation is high (such as noon) or when electricity demand is low (such as in the morning), the electricity demand may exceed the solar power generation. In such cases, the excess electricity is typically fed back into the grid. From the perspective of independent solar power, after solar power generation during the day, a portion of it can be used for household consumption. However, during periods of high solar power generation, such as at noon or when electricity demand is low in the morning, the electricity demand may exceed the solar power generation. Therefore, the excess electricity is used for grid connection to earn electricity fees
- Independent energy storage is charged twice a day, namely, once in peacetime and once in off-peak electricity price. When the peak electricity consumption is greater than the discharge electricity consumption, the energy storage discharge is all used for peak discharge to realize peak-valley price difference arbitrage. When the discharge electricity consumption is greater than the peak electricity consumption but less than the domestic electricity consumption, the energy storage will be partially used for regular discharge. When the discharge power is greater than the domestic power, if there is arbitrage space (the charging price is less than the on-grid price), it can be used for on-grid arbitrage.
- In the integrated solar and energy storage system, solar power generated is used for self-consumption and charging. Depending on the household electricity consumption and discharge requirements outlined (2), it can choose peak discharge during peak hours, discharge during regular hours, or feed excess electricity back into the grid to earn electricity fees.
Economy and Sensitivity Analysis of Terminal Household Storage Products
Based on the calculation, European countries have the highest economy, and the optical storage integrated machine products have the highest economy
According to the internal rate of return of each product, Optical storage machine > photovoltaic > energy storage. If it is not equipped with photovoltaics, energy storage is basically uneconomical, and its income comes from peak discharge, but it needs to be charged during valley, so there is limited arbitrage space by peak-valley price difference alone. Compared with photovoltaic, optical storage integrated machine can improve the self-use rate and overall consumption rate of photovoltaic power generation through energy storage, so as to have relatively higher available power generation. Compared with energy storage, charging can come from photovoltaic power generation, reducing part of charging cost.
Judging from the internal rate of return of various countries, Europe and the United States have higher rates of return, and the economy of all-in-one optical storage machine is higher.
According to the recycling cycle, the return cycle of all-in-one optical storage machines in the United States is 7 years, and that in Germany, Italy, France and Britain is 4-7 years.
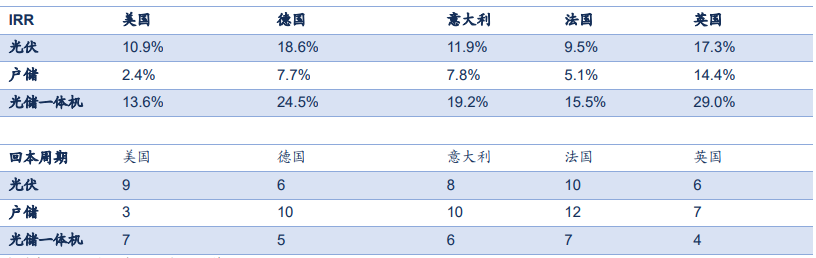
Figure 2: IRR calculation of various countries and calculation of this cycle
Taking the United States as an example, it is estimated that the total cost decreases by 5% and the IRR increases by about 1.7 pct, and the marginal effect increases with the increase of the cost decrease
The benefits of the decrease in total cost to the optical storage system are reflected in two aspects, one is the decrease in initial investment, and the other is the decrease in maintenance cost and battery replacement cost. The decrease in total cost can be said to be the most direct way to increase IRR and improve the economy of optical storage system. Some American regional policies give cash subsidies to users who purchase optical storage systems. For example, Arizona announced that within three years from May 1, 2018, users who purchase and install qualified battery energy storage systems and participate in SRP battery research programs can receive subsidies of up to US $1,800. Government subsidies are actually equivalent to reducing total costs and improving economy. From the impact of IRR, government subsidies will greatly improve the economy of household storage system, thus improving the purchasing enthusiasm of residents.
In addition, we can see that the increase effect of cost reduction (other conditions unchanged) on IRR has a marginal effect enhancement law, with cost reduction ranging from 0% to 5%, IRR increasing by 1.7 pct, cost reduction ranging from 20% to 25%, IRR increasing by 3.8 pct. IRR is a discount rate equal to the present value of initial investment and future cash flow, and the discount effect of discount rate on future cash flow decreases marginally. Therefore, although the amount of reduction is the same, the lower the initial investment, the greater the IRR increase.
In the future, the cost will be gradually reduced, the improvement of IRR will become more obvious, and the economy will promote the development of household storage more rapidly.
Other conditions unchanged, the electricity price increased by 0.1 USD/kWh and the IRR increased by about 1pct
The impact of electricity price on IRR is actually to improve the income of saving electricity charges of optical storage system. The higher the electricity price, the higher the electricity cost of consumers, and the higher the income of the corresponding optical storage system. The effect is linear. The increase of electricity charges will increase all income in a fixed proportion, and the income structure of household storage will not change.
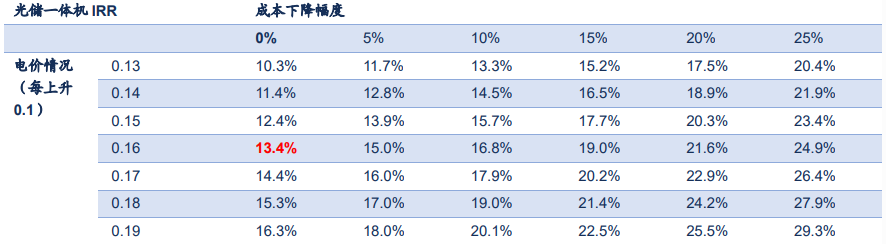
Figure 3: Cost and electricity price sensitivity analysis of solar energy storage
systems in the United States
Other conditions remain unchanged, the per capita electricity consumption will increase by 50kWh/month, and the IRR will increase by about 0.9 pct, and the marginal effect will be limited by the scale of optical storage system
The increase of per capita electricity consumption is the substitute space for domestic electricity consumption by optical storage system, which can be divided into two parts, one is that the original on-grid electricity consumption is used for domestic electricity consumption, and the other is that the increase of peak electricity demand will increase the income. However, this effect will eventually be limited by the scale of the optical storage system. If the household electricity consumption reaches a certain amount, the income of the optical storage system has been maximized (the electricity consumption substitution is full at peak hours and the electricity consumption substitution is full at ordinary times). At this time, increasing the per capita electricity consumption can no longer improve the rate of return.
If conditions remain unchanged, the peak-valley price difference increases by 5%, and the IRR increases by about 0.7 pct
The impact of peak-valley price difference on IRR is mainly to improve the income of energy storage, which is embodied in the reduction of charging cost during valley and the improvement of discharge income during peak. This effect is linear and there is no structural change.

Figure 4: The core of the development of household storage system lies in the rate of return
The core of the development of household storage system lies in the rate of return, and according to the analysis, it can be concluded that the core influencing factors of the rate of return of optical storage system are:
- Electricity price for residents
- Peak-valley price difference of electricity
- Per capita living electricity consumption
- Household storage system cost
Among them, the sensitivity of household storage system cost and residential electricity price is high.
The Economic Efficiency of Integrated Solar and Energy Storage is Improving, with Relatively Higher Economic Efficiency in the European and American Markets-China.exportsemi.com


![Hot news-[Event Preview] Registration Open for the 2025 International New Energy Industry Marketing Summit](https://bandaoti.oss-rg-china-mainland.aliyuncs.com/uploads/20241219/6fb4f075d1bd126de113312b3f1ff596apgwZt567SmoqfCW.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_210,w_370,limit_0)



