On Nov. 8, chipmaker Nvidia officially replaced Intel in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a well-known stock market index that includes 30 publicly traded companies that are considered representative of U.S. business and industry. Nvidia replaces Intel in the Dow Jones This move underscores the growing importance of AI in the economy. So, why does Nvidia stand out in the AI era? What are its coping strategies?
Nvidia was initially known for its graphics processors, which mainly served gamers. But in 2016, Nvidia took a decisive step by introducing the first AI-specific GPU architecture. These GPUs can not only handle complex image rendering, but also efficiently complete the large amounts of computation required for AI training.
This transformation has allowed Nvidia to quickly become a core player in the AI space, especially in training large language models (LLMs) and generative AI such as ChatGPT. According to GlobalData's innovative analytics platform, Technology Foresights, Nvidia is particularly prominent in key technology areas. For example, the company has 40 percent more patents for generative AI than Intel and has pioneered dedicated accelerator technologies that support LLM training and inference, such as variational autoencoders (VAEs) and neural network accelerators. These technologies have earned NVIDIA an unshakable position in the market. NVIDIA's success comes not only from hardware performance, but also from its keen insight into future trends and its quick action. For example, it deployed AI accelerators early on, developing solutions that support a wide range of AI tasks, from text generation to image processing. This forward-looking position has given Nvidia an unshakable position in the AI revolution.
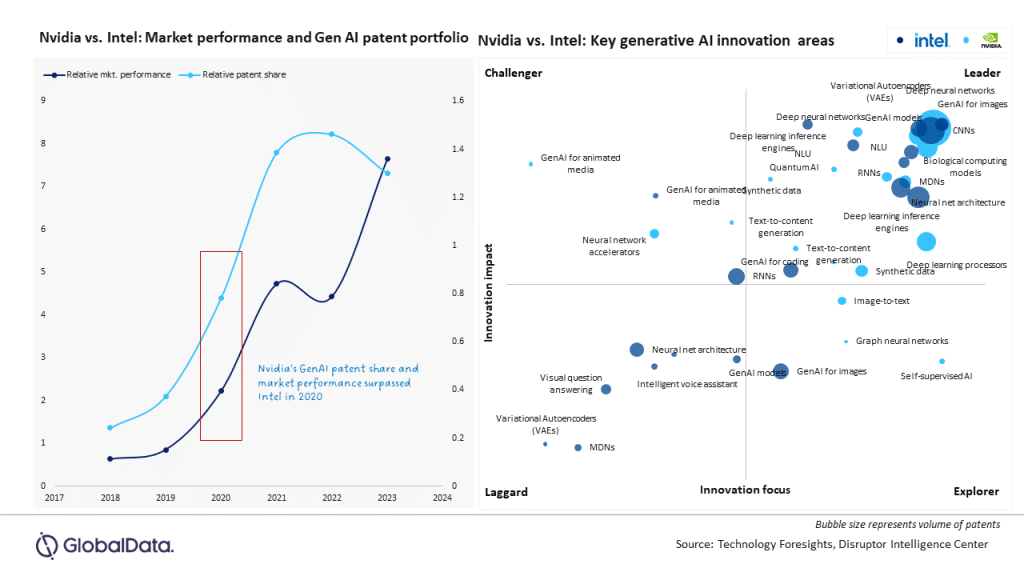
Figure: Nvidia replaces Intel on the Dow Jones Index (Source: GlobalData)
In contrast, Intel has always been the hegemon in the traditional CPU field, but with the rise of AI technology, this CPU-centric computing model is starting to seem inadequate. The efficiency of GPUs in handling AI tasks has left Intel falling behind on new tracks.
That doesn't mean Intel isn't taking action, though. In recent years, it has also accelerated its transformation into the field of AI. For example:
AI chip development: Intel launched the Habana Gaudi processor designed for AI applications in an attempt to capture a piece of the training and inference market.
Investing in quantum computing: In terms of future computing technology, Intel also sees the potential of quantum AI and is deploying related applications.
Partnering with key customers: By partnering with Google, Meta and other companies, Intel hopes to find a breakthrough in the AI market with large-scale data center applications.
Still, Intel's challenges remain daunting. On the one hand, NVIDIA, the leader in the GPU market, has firmly controlled the industry's right to speak; On the other hand, other emerging players such as Google's Tensor processors and start-up SambaNova are also competing for the AI chip market.
Nvidia replaced Intel in the Dow Jones Industrial Average, which is not only a change in the market landscape, but also a microcosm of technological development in the AI era. In this technology race, whoever can continue to lead innovation will be able to occupy a greater voice in the future semiconductor landscape. As GlobalData analysts say, innovation is the eternal driving force for technological progress, and no matter how the leaders change, the continuous breakthrough of computing power will continue to lead the global development.






