Currently, specialized machine learning tools and frameworks have gone through a cycle from popular to hard-to-scale and production-ready tools, and many emerging tools have gained some traction in the market, but still face the problem of transitioning from experimental to production. In particular, after the explosive growth of Vector Database, its uniqueness in vector space search is no longer attractive. Traditional database vendors have introduced their own methods of vector search, and cloud giants such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have extended their native database services to support vector search and retrieval at scale.
The commercialization process of AI agents
On the AI agency side, while some companies are secretive about their projects, we've seen multiple attempts at commercialization of AI agents. Touted as "the first AI software engineer," Devin by Cognition is able to plan and execute tasks that require thousands of decisions, fix errors, and learn along the way. After its launch, Devin was well received by investors, successfully reaching a valuation of $2 billion within six months, although the product had some problems that required manual intervention and control
In addition, OpenDevin, as Devin's open source competitor, has already led Devin by 13 percentage points in the software engineering benchmark (SWE-bench). Another company, MultiOn, is also investing heavily in reinforcement learning (RL), with its autonomous web proxy, Agent Q, which will combine search, self-criticism, and reinforcement learning, and is expected to be released later this year. At the same time, Meta's TestGen-LLM also quickly moved from concept to product, integrating into Qodo's Cover-Agent in just four months.
AI-powered search is starting to break the mold, but it still faces growing pains
In the AI-driven search space, Perplexity is the most high-profile AI search start-up with a $165 million funding round. At the same time, Google has also begun to roll out search snippets based on its Gemini technology. However, these companies are facing reliability issues, with Perplexity facing the same challenges as other LLM-based services in dealing with "hallucination", and Gemini being found to have cited satirical Reddit posts as a source of advice (e.g., "Eat a rock a day"). These problems make AI search still a big challenge.
Copyright issues are controversial: creators versus model builders
With the rapid development of generative AI, copyright issues have become an ongoing point of contention. Media organizations, music companies, and content creators have raised strong questions about modelbuilders using their content for training. To ease this tension, companies such as OpenAI and Google are in talks with major media outlets seeking to resolve copyright issues through licensing agreements. Some startups have chosen to circumvent these controversies altogether and advocate for ethical certification programs, such as the Fairly Trained program, founded by former Stability AI executive Ed Newton-Rex.
Some companies have adhered to a "fair use" stance and expressed less willingness to compromise with critics. As the difficulty of data acquisition increases, the problem of YouTube video scraping has become the focus of public opinion. OpenAI has been accused of using YouTube videos for audio transcription training, while organizations such as Eleuther AI have also been revealed to have used a large number of YouTube subtitles as training data.
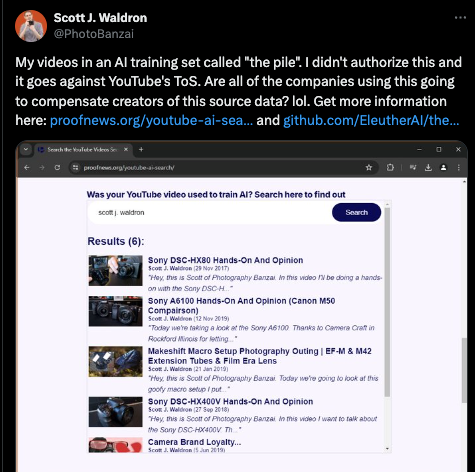
Figure: Generative AI copyright issues have sparked controversy
The court's decision is vague and copyright issues remain unresolved
The legal question of whether the model builder infringes the creator's copyright remains unanswered. Despite the courts, model builders have so far managed to dismiss a number of extensive copyright claims, leaving only a portion of the original data scraping claims. Companies such as Adobe, Google, Microsoft and OpenAI have taken unusual steps to provide copyright protection to their customers to avoid possible legal risks.
Autonomous driving: The rapid development of Wayve and Waymo
After several years of ups and downs, the autonomous driving industry is recovering. Wayve raised $1.05 billion in Series C funding through funding, while Waymo expanded its operations in multiple cities across the United States. Waymo has already seen gradual expansion in San Francisco, Los Angeles and Phoenix, with plans to enter the Austin market later this year. In addition, Waymo's technology is also beginning to show commercial potential, and Alphabet announced an additional $5 billion investment in Waymo to further support its operations and technology research and development.
However, autonomous driving is still a risky industry. Last year, an accident involving a self-driving car that injured a pedestrian caused the company to lose its operating license and underwent a major change in leadership. Despite this, General Motors decided to inject $850 million into Cruise and retest it.

Figure: Autonomous driving and still unsafe factors
Humanoid robots: Investments are pouring in, but there are technical bottlenecks
The field of humanoid robots has also ushered in significant investment. Startups like Figure, Sanctuary, and 1X have raised close to $1 billion in funding from big names like Samsung, Microsoft, Intel, OpenAI, and NVIDIA. However, humanoid robots still face many technical challenges, especially in terms of replicating the complexity and engineering flexibility of human movement, which past attempts have often failed and costly.
These startups are looking to overcome these bottlenecks through advanced visual language models (VLMs), real-world training data, simulation, and more efficient hardware. Still, the question of whether humanoid robots can provide greater efficiency than cheaper, non-human-like industrial robotic systems remains an open question.
Summary
The field of AI is undergoing a profound transformation, with technological innovations emerging one after another, but also with various challenges. Whether it's the expansion of machine learning tools, the commercialization of AI agents, or investments and technological breakthroughs in autonomous driving and humanoid robots, companies are accelerating. However, difficulties in copyright issues, technical bottlenecks and legal disputes still need to be resolved, and the development of the entire industry is still full of uncertainties. In the next few years, the maturity and market acceptance of these technologies will determine whether they can truly break through the current bottleneck and achieve full commercial application.
Related:






